The main factors affecting the performance of polyurethane foams
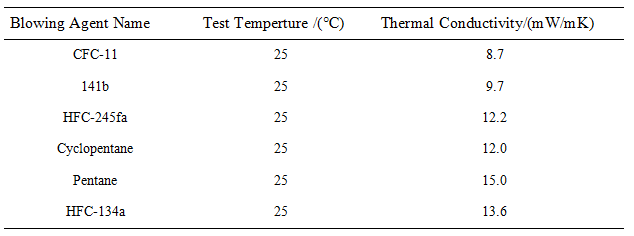
1. Factors affecting the bulk density of PU foam:
The amount of foaming agent, temperature, foaming gel speed and the thickness of foam products,etc.
The most important factors are the amount and temperature of foaming agent. The following is an example of the foaming agent content:
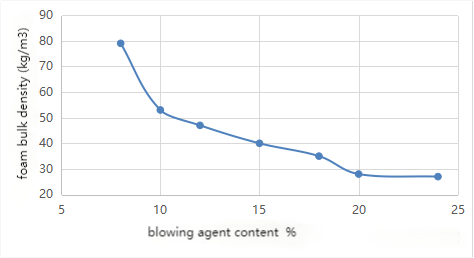
2. Factors affecting the compressive strength of PU foam:
The bulk density, isocyanate index, hydroxyl number and functionality, polyol varieties, cell direction and temperature, etc. Here we mainly talk about bulk density, isocyanate index and cell direction.
2.1 The effect of bulk density on the compressive strength of PU foam, as below:
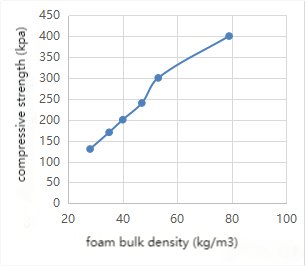
2.2 The effect of isocyanate index on compressive strength:
Under many conditions, the compressive strength of PU foam increases with the increase of the isocyanate index. The reason is that the index increases, the degree of crosslinking increases, and the content of urea carbamate increases, but it decreases when it exceeds a certain range, mainly because it is too brittle.
2.3 The effect of cell direction on compressive strength:
Because the cells of PU foam are basically oval, the smaller the bulk density of the foam, the more obvious the directionality of the bubbles. The compressive strength of the long axis of the bubble is higher than that of the minor axis, that is, the compressive strength of the foam growth direction is the highest.
3. Factors affecting thermal conductivity
The main factors are bulk density and blowing agent type.
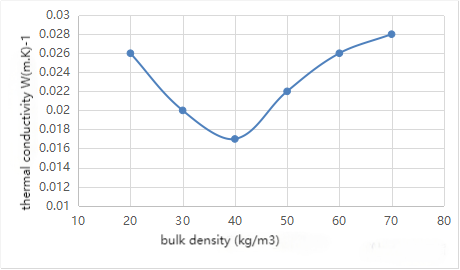
3.1 Bulk density
The bulk density of the PU insulation board we are now used as thermal insulation material is generally 30-40kg/m3, and the bulk density is too high or too low to have a significant impact on its thermal conductivity. The following figure shows the relationship between bulk density and thermal conductivity.
3.2 Blowing agents
The thermal conductivity of PU foam used as an insulation material is about 70% depending on the thermal conductivity of the gas filled in the pores, so the thermal conductivity of the foaming agent itself directly affects the thermal conductivity of the material. The thermal conductivity of various blowing agents is as follows: